07 Aug The Future of Regenerative Medicine in Orthopedics
Regenerative medicine represents one of the most promising frontiers in orthopedic treatment today. This groundbreaking field aims to heal damaged musculoskeletal tissues by harnessing our body’s innate capacity to regenerate itself.
As researchers unlock the secrets of stem cells, biomaterials, and tissue engineering, regenerative techniques offer new hope for restoring joint function and mobility. These innovative biological therapies provide a much-needed alternative to traditional surgical joint replacements and mechanical implants.
In this article, we will explore the tremendous potential regenerative medicine holds for revolutionizing orthopedic care. We will examine current clinical applications, glimpse exciting future technologies on the horizon, and discuss how regenerative treatments could transform the management of common orthopedic injuries and degenerative conditions.

The Power of the Body to Heal Itself
At its core, regenerative medicine seeks to restore the body’s natural healing abilities. This involves stimulating internal repair processes to generate new, healthy tissue or regenerate damaged organs.
Rather than relying solely on synthetic implants or artificial joints, regenerative techniques harness our body’s spectacular capacity for self-renewal. Stem cells, growth factors, biomaterials and bioengineering are all tools to jumpstart and enhance the body’s intrinsic power to heal.
Regenerative Approaches Take Root in Orthopedics
Regenerative therapies are quickly moving from the realm of science fiction into orthopedic reality. Current clinical applications include restoring cartilage defects using cell therapies, rebooting tendon regeneration with platelet-rich plasma, and integrating 3D-printed biomaterials to foster bone repair.
According to a study published in the journal Regenerative Medicine, stem cells could be effective in reducing pain and improving function in patients with osteoarthritis.
The study found that stem cells could be a promising treatment for osteoarthritis
Exciting Advances on the Horizon
Looking ahead, there is tremendous enthusiasm surrounding forthcoming regenerative therapies for orthopedics. Novel cell-based treatments, sophisticated biomaterials and breakthroughs in bioengineering herald the next generation of biological joint repair.
One particularly exciting technology – 3D bioprinting – offers the eventual possibility of on-demand printed tissues and cartilage. As innovations in regenerative medicine accelerate, the goal of biologically restoring optimal joint function appears increasingly attainable.
The Future of Orthopedic Care

Regenerative therapies represent the vanguard ushering in a new paradigm for orthopedics. The future is moving away from mechanical joint replacements and towards harnessing our body’s innate capacity for healing and renewal. As researchers optimize regenerative technologies, they edge closer to the ultimate goal – fully restoring joints’ natural form and function using our own tissues.
For many conditions once considered irreversible, regenerative medicine provides cause for hope. The human body has tremendous untapped potential for regeneration. Unlocking its secrets today paves the way for the orthopedic treatments of tomorrow.
For millions suffering joint pain and loss of function, the promise of regenerative medicine burns bright.
Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cell therapy involves the injection of stem cells, which are undifferentiated cells that can develop into many different cell types into damaged tissues. The stem cells then differentiate into the required enclosures to heal the tissue.
Stem cells can be obtained from bone marrow, adipose tissue, or donated umbilical cord blood. They are being extensively researched for orthopedic applications such as:
- Treating cartilage injuries and osteoarthritis
- Repairing tendon and ligament tears
- Regenerating bone in fractures, bone defects, and non-unions
- Improving outcomes after orthopedic surgeries
Research indicates that stem cell therapy may reduce inflammation, promote cartilage regeneration, and improve knee function in osteoarthritis patients.
Regenerative medicine therapy doctors are effectively utilizing stem cells for a variety of orthopedic applications. Clinical trials show promising results for stem cell therapy in treating conditions like cartilage injuries, osteoarthritis, and tendon tears.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy
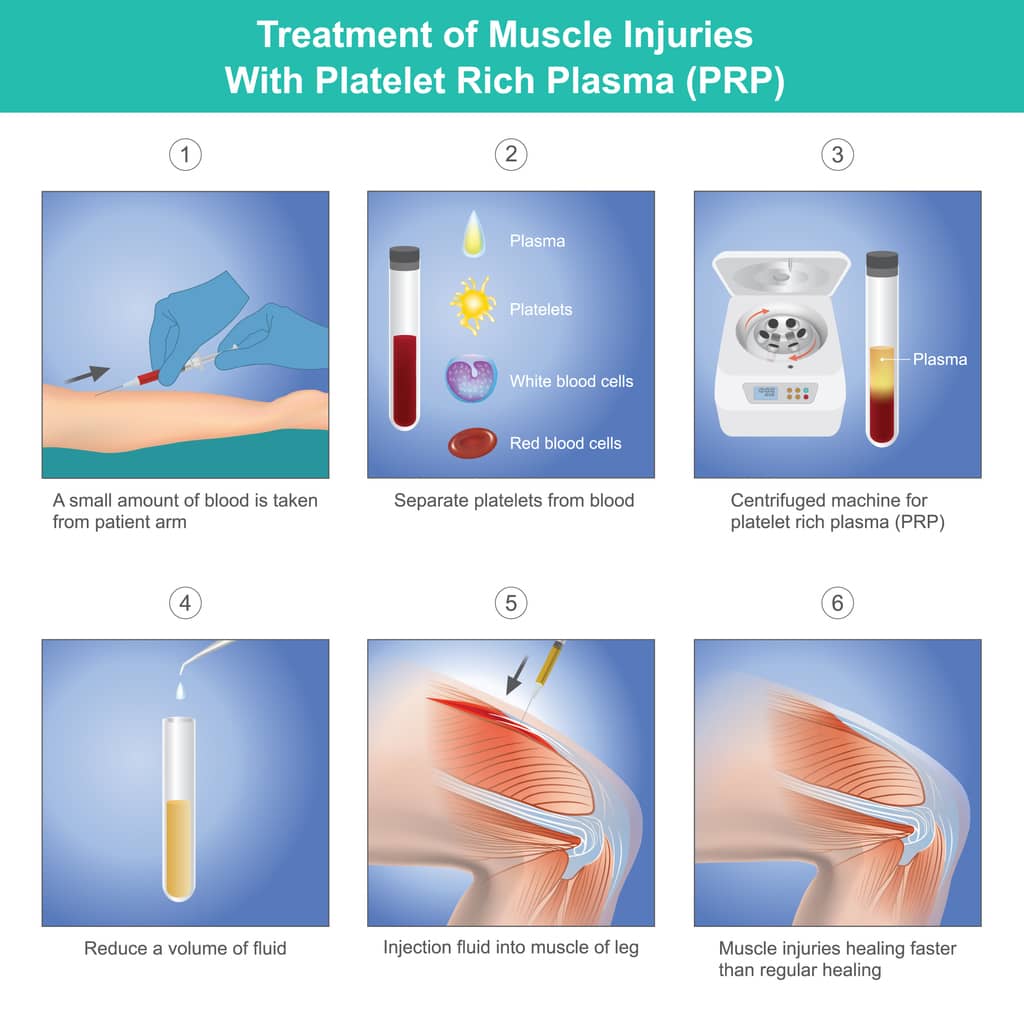
PRP involves isolating plasma with a high concentration of platelets from a patient’s blood and injecting it into the injured area. The concentrated platelets release growth factors that stimulate healing.
PRP is being used to treat:
- Tendon and ligament injuries
- Osteoarthritis
- Muscle strains
- Bone injuries
According to a review, PRP reduces pain and improves joint function in knee osteoarthritis. Early results also suggest it may help regenerate cartilage.
Tissue Engineering
Tissue engineering techniques use scaffolds, cells, and biochemical signals to regenerate damaged tissues.
Some orthopedic applications include:
- Bioengineered cartilage for cartilage repair
- Engineered bone grafts for bone regeneration
- Scaffolds seeded with stem cells to heal tendons, ligaments, and cartilage
- 3D bioprinting of musculoskeletal tissues
Research shows bioengineered cartilage scaffolds successfully regenerate hyaline-like cartilage in animal models. Several products are in clinical trials.
Case Studies and Clinical Trials
The results of early clinical trials provide a reason for optimism regarding the potential of regenerative medicine in orthopedics. Some promising findings include:
Stem Cell Therapy for Knee Osteoarthritis
A clinical trial published in Stem Cell Research & Therapy evaluated the safety and efficacy of intra-articular injection of allogeneic adipose-derived stem cells ELIXCYTE® for knee osteoarthritis.
PRP Therapy for Rotator Cuff Injuries
A trial investigated PRP injections to treat chronic rotator cuff tendon tears. Patients received either PRP or placebo injections under ultrasound guidance.
After six months, the PRP group showed improved shoulder function, reduced pain, and higher rates of tendon healing compared to placebo.
Stem Cell Therapy for Cartilage Defects
A study evaluated stem cell therapy’s safety and preliminary efficacy for cartilage defects in the knee.
Patients received injections of cultured stem cells under ultrasound guidance into knee cartilage lesions. After an average 26 months follow-up, treated defects showed significant filling and regeneration of hyaline-like cartilage. Pain and symptoms also improved.
These and other early results indicate regenerative medicine could become first-line therapies for common orthopedic conditions.
The Future of Regenerative Medicine in Orthopedics

The field of regenerative medicine is rapidly evolving. Some of the advancements and trends that may shape the future of regenerative orthopedics include:
Advanced Cell Therapies
Researchers are exploring innovative stem cell therapies involving gene editing, reprogramming, and activation of endogenous stem cells to enhance regenerative capabilities.
Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) that can differentiate into many cell types are also being actively studied for orthopedic applications.
Combination Therapies
Future treatments may combine cell therapy, biomaterials, and bioactive molecules to optimize the regenerative response. For example, delivering cells using 3D printed scaffolds containing controlled drug release.
Advanced Biomaterials
Improved biomaterials and fabrication methods like 3D bioprinting will facilitate the development of ‘smart’ scaffolds that interact with cells and release biological factors in response to environmental stimuli to promote regeneration.
Enabling Technologies
Advances in nanomedicine, drug delivery, gene editing, and cell reprogramming will enable more sophisticated regenerative therapies.
Clinical Translation
Significant work remains to improve the clinical translation of promising experimental therapies into safe, effective, and economically viable treatments. However, the field is rapidly advancing. With continued research and investment, some experts predict regenerative techniques could begin to enter mainstream orthopedic practice within the next 5-10 years.
Early commercialization efforts are underway, with several biotech startups focusing on bringing regenerative products to market. For example, Histogen has developed a next-generation stem cell treatment for knee cartilage injuries in Phase 3 trials.
As regenerative medicine progresses from proof-of-concept to clinical adoption, some of the key steps along the path will include:
- Optimization of cell sourcing and preparation protocols
- Developing cost-effective GMP production and manufacturing processes
- Conducting large randomized clinical trials to demonstrate efficacy and long-term safety
- Evaluating health economics to demonstrate cost savings versus traditional treatments
- Establishing regulatory approval pathways with agencies like the FDA
- Training orthopedic surgeons in the application of regenerative techniques
The future looks bright for regenerative medicine in orthopedics. With continued research and funding, regenerative treatments have the potential to become mainstream and provide customized biological solutions for injuries, degeneration, and arthritis.
As regenerative medicine therapy becomes more established, experts predict it will gradually enter mainstream orthopedic practice over the next decade. Regenerative medicine clinics and therapy doctors will play a key role in bringing these advances to patients through customized treatment protocols.
Market Analysis and Future Trends
The orthopedic regenerative medicine market is experiencing rapid growth, fueled by increasing demand for biologic treatments that offer the potential for true tissue repair and regeneration.
Several key factors underpin the projected future growth:
- Orthopedic Regenerative Surgical Products Market Report, 2030 size to grow from USD 4.2 billion in 2021 to USD 5.9 billion by 2030, at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 3.9% during the forecast period.
- There is high demand for less invasive alternatives to joint replacement surgery that can provide lasting results, and avoid implant complications.
- An aging population suffering from orthopedic problems will drive demand for regenerative treatments.
- The U.S. dominates the orthopedics regenerative medicine sector, holding over 40% of the global market share. However, Europe and Asia-Pacific represent growing markets.
- Continuous technology advances, research funding, and investments in commercialization will enable the transition of emerging therapies into viable products.
Major companies already active in this space include Medtronic, Stryker, Zimmer Biomet, and NuVasive. In the future, strategic partnerships between big medical device players, biotech startups, and academic institutes will likely accelerate development.
Overall, the market outlook for regenerative medicine in orthopedics appears very positive. With multiple growth drivers, regenerative treatments are poised to capture more of the orthopedic solutions market.
Conclusion
Regenerative medicine holds tremendous promise in revolutionizing the field of orthopedics. Ongoing studies suggest that the utilization of stem cells, growth factors, bioengineered tissues, and other groundbreaking biologics might offer effective avenues for regenerating damaged musculoskeletal tissues, which have historically posed challenges in the healing process.
While still early days, the results of initial clinical studies and trials are extremely promising. As research progresses rapidly, there is reason for optimism that regenerative techniques will steadily transition into mainstream orthopedic practice over the next decade.
Driven by rising demand, continuous technological advances, research funding, and commercialization efforts, regenerative medicine is poised for robust global growth. In time, regenerative treatments could make joint replacement surgery in younger arthritic patients obsolete.
The future of orthopedic care involves moving beyond temporary implants and mechanical devices toward biologically restoring the structure and function of musculoskeletal tissues. Regenerative medicine looks set to play a starring role in making this future a reality.


No Comments